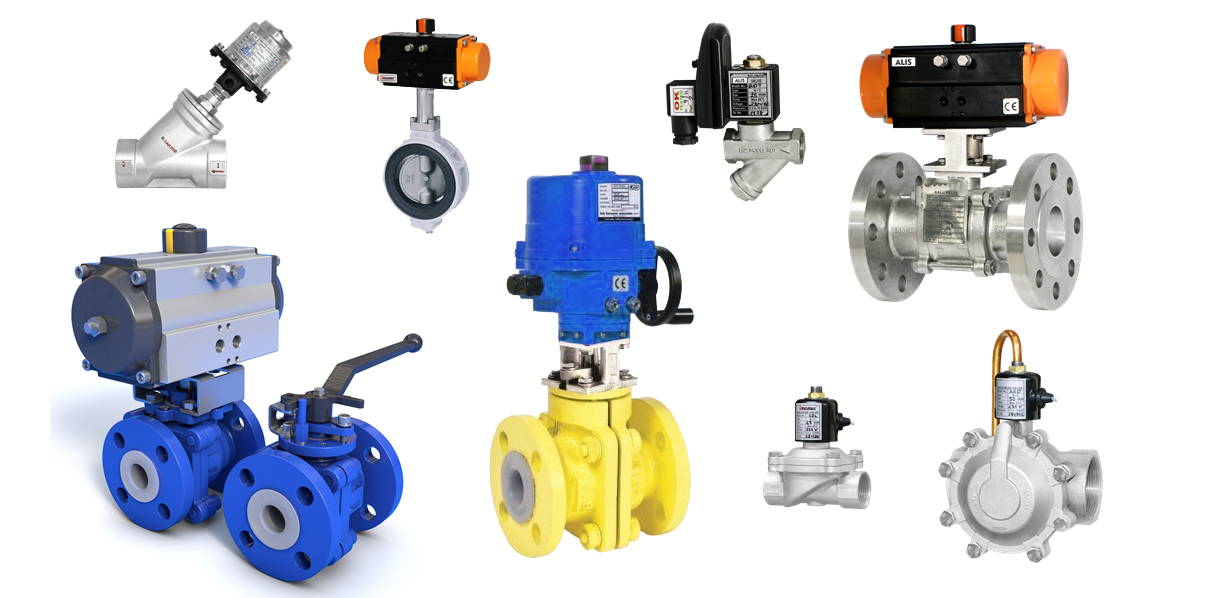
In the vast world of Industrial Manufacturing, where machines hum and factories buzz with activity, one crucial player in the symphony of production is often overlooked – the humble Control Valve. These unassuming devices play a vital role in managing and fine-tuning the intricate dance of processes within the heart of manufacturing units. Let’s take a journey into the world of Control Valves, unraveling their significance and demystifying their functions.
“Control Valves: The Silent Maestro of Manufacturing Efficiency.”
Understanding Control Valves
Control Valves are like conductors in an orchestra, guiding the flow of fluids within a manufacturing system. They regulate the rate, volume, and pressure of liquids or gases, ensuring that the production process hits all the right notes. Picture them as the traffic controllers of an industrial highway, directing the flow of materials with precision.
The Basics of Operation
In simple terms, a Control Valve opens, closes, or partially obstructs the passage for fluids based on signals it receives. These signals, often electronic or pneumatic, dictate the valve’s movement. It’s akin to a faucet – turning it to control the water flow. Similarly, a Control Valve modulates the flow of substances to maintain optimal conditions in the production line.
Types of Control Valves
Diving deeper, we encounter various types of Control Valves, each tailored to specific industrial needs. Let’s explore a few of them:
1. Butterfly Valves
Resembling a butterfly’s wings, these valves pivot to control flow. They are quick to operate, making them ideal for large-scale applications where swift adjustments are crucial.
2. Globe Valves
Globe Valves regulate flow by moving a disc into or out of the fluid path. Think of them as the dimmer switches, offering precise control over the amount of substance passing through.
3. Ball Valves
With a simple design, Ball Valves use a rotating ball to start, stop, or regulate fluid flow. They are reliable and find utility in situations demanding tight shut-off.
Significance in Industrial Manufacturing
Now, let’s delve into why Control Valves are the unsung heroes of Industrial Manufacturing.
1. Precision in Production
In a manufacturing setup, precision is paramount. Control Valves allow for fine-tuning the flow rates, ensuring that the right amount of raw materials reaches each station, contributing to high-quality output.
2. Energy Efficiency
By controlling the flow of materials, these valves contribute to energy efficiency. They help maintain optimal conditions, reducing energy wastage and minimizing the environmental impact of industrial processes.
3. Process Stability
Imagine a manufacturing process as a delicate balancing act. Control Valves play a crucial role in maintaining stability, preventing fluctuations that could lead to defects in the final product.
Technological Advancements
As technology advances, so do Control Valves. Modern iterations come equipped with sensors and smart controls, transforming them into intelligent components of the manufacturing ecosystem.
1. Digital Control Systems
Integrated digital control systems enable precise adjustments, responding to real-time data. It’s like upgrading from a manual thermostat to a smart, automated climate control system.
2. Remote Monitoring
Control Valves can now be monitored and adjusted remotely, reducing the need for constant on-site supervision. This not only improves efficiency but also enhances worker safety.
Challenges and Solutions
No journey is without its challenges. Control Valves face issues such as wear and tear, corrosion, and potential malfunctions. However, ongoing research and development strive to address these concerns.
1. Material Innovation
Scientists and engineers are exploring new materials to enhance the durability and longevity of Control Valves. Think of it as upgrading from traditional materials to futuristic, resilient alloys.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Advancements in predictive maintenance techniques use data analytics to anticipate issues before they occur. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures the continuous flow of production.
Practical Application
Let’s imagine a practical scenario to understand the importance of Control Valves in Industrial Manufacturing. Picture a chocolate factory where precise measurements are crucial. The Control Valves in this setup regulate the flow of ingredients like cocoa and milk, ensuring the perfect blend for that delectable chocolatey taste. Just like a skilled chef adjusting seasoning in a recipe, these valves guarantee consistency in each batch, making sure every chocolate bar meets the highest quality standards.
Real-world Impact
Now, think about a manufacturing plant that produces medical devices. Control Valves in this context play a critical role in the precise mixing of pharmaceutical components. Imagine the impact of an error in this process – it could result in faulty medical devices, potentially jeopardizing patient safety. By using Control Valves, the production line maintains accuracy, ensuring that every medical device meets stringent quality requirements, contributing to the well-being of end-users.
“In the world of production, precision is the key, and Control Valves hold the baton to orchestrate it flawlessly.”
Conclusion
In the grand tapestry of Industrial Manufacturing, Control Valves are the unsung conductors, orchestrating a flawless performance. From regulating the flow of fluids to embracing cutting-edge technology, these valves are the heartbeat of efficient and sustainable production. So, the next time you witness the seamless operation of a manufacturing unit, remember the silent maestro – the Control Valve – making it all possible.