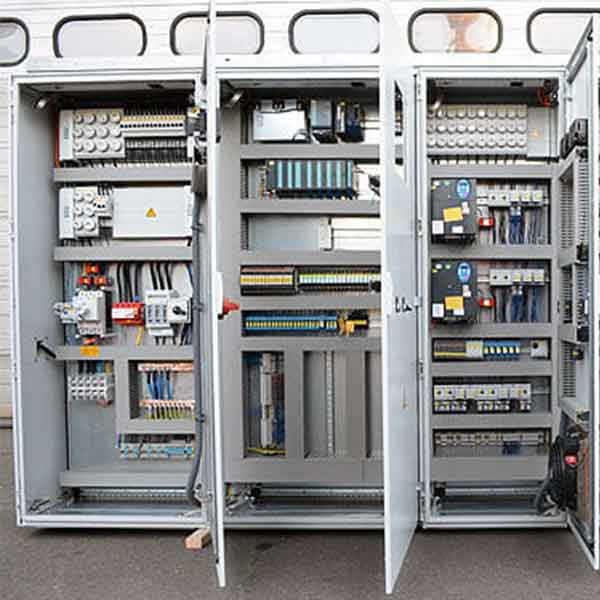
In the world of making things, one crucial aspect is often overlooked but plays a big role – Panel Design and Fabrication. This article will take you on a journey through the ins and outs of mastering this craft in the realm of Industrial Manufacturing.
“Crafting the future of industry through precise Panel Design and Fabrication.”
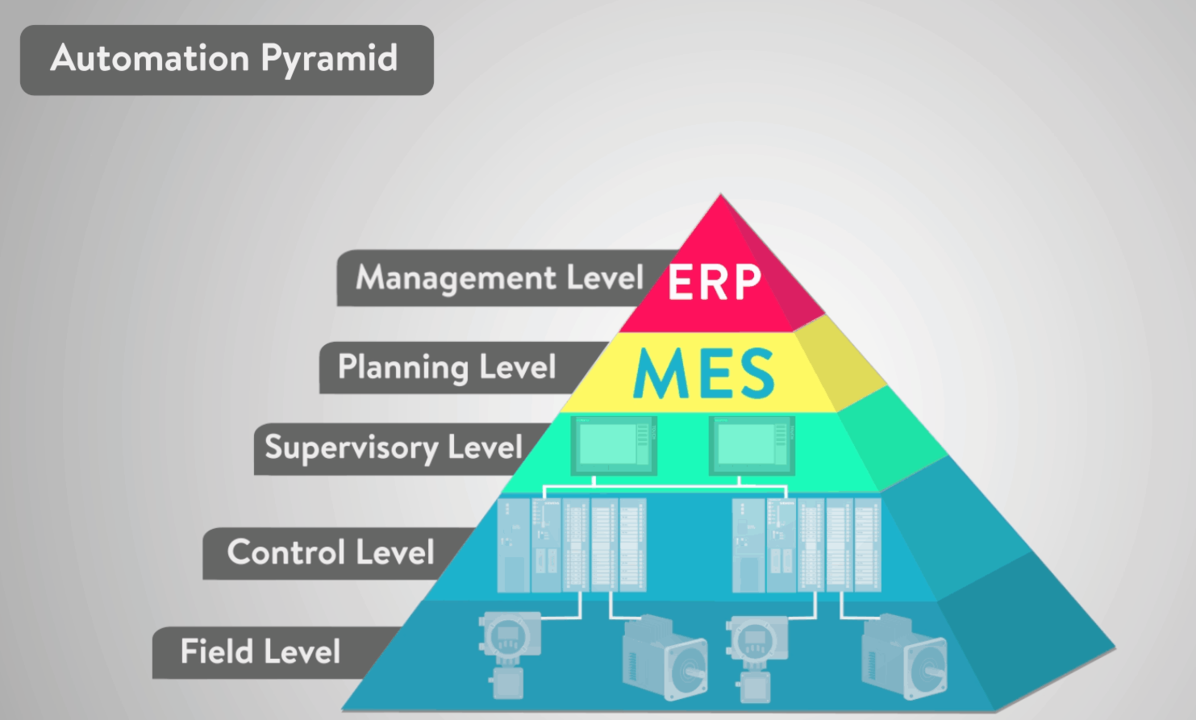
Understanding Panel Design
Let’s start with the basics. What is Panel Design? In simple terms, it’s like planning the layout of a puzzle. Engineers draw a blueprint, deciding where each piece fits. These ‘pieces’ are the various components and instruments that make a machine tick.
The Blueprint Magic
The blueprint is like the map of a treasure hunt – it guides workers to put everything in the right place. Engineers use special computer software to create these blueprints. It’s like using a super-smart digital sketchpad to plan how machines will look and function.
Nuts and Bolts of Fabrication
Once the blueprint is ready, it’s time to turn plans into reality – that’s where Fabrication comes in. Imagine building a robot from LEGO bricks. Fabrication is like snapping those bricks together, but on a much larger scale.
Crafting with Care
Skilled workers cut, bend, and weld sheets of metal, creating the panels outlined in the blueprint. It’s a bit like sculpting, but instead of clay, they use sturdy materials like steel or aluminium.
Precision Matters
Precision is key in fabrication. It’s not just about making things look good; it’s about making sure every piece fits perfectly. If one part is off, the whole machine might not work as intended. It’s like assembling a puzzle – one wrong piece, and the picture doesn’t come together.
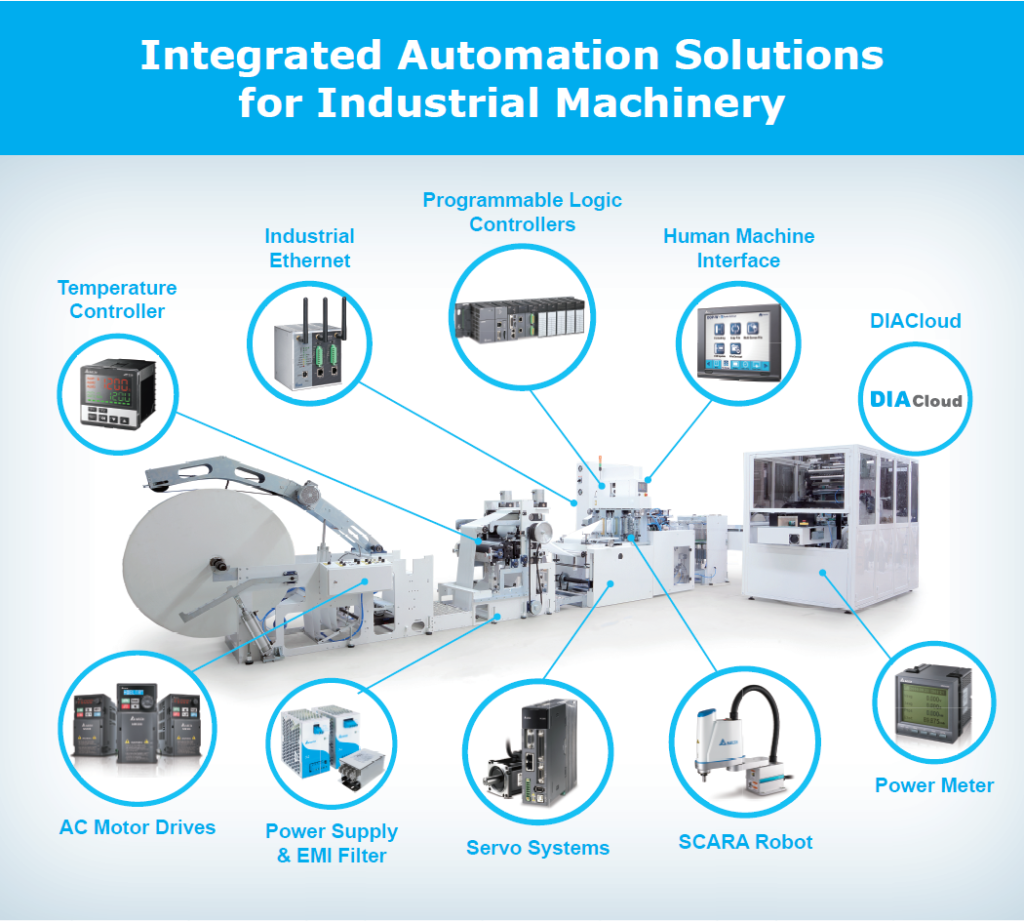
The Dance of Electronics
Now, let’s talk about the electronic dance happening behind those panels. Imagine the panels as the stage, and the electronic components as the performers. They need to work in harmony to create the final masterpiece.
Wiring Wonders
Behind the scenes, skilled technicians connect wires like conductors leading an orchestra. Each wire has a specific role, and connecting them correctly ensures the machine sings its song smoothly.
Testing, 1-2-3
Before a machine hits the production line, it undergoes rigorous testing. It’s like a dress rehearsal for a play. Engineers check if every button, light, and switch does its job. This step ensures the final product is ready for its starring role.
Industry Innovations
The world of Panel Design and Fabrication is always evolving. New technologies constantly emerge, making machines smarter, faster, and more efficient.
Smart Panels
Imagine a panel that not only controls a machine but also learns from its performance. Smart panels can adapt and optimize processes, making industrial manufacturing even more efficient.
Sustainable Fabrication
In today’s world, being eco-friendly is crucial. Engineers are exploring materials and techniques that reduce environmental impact. It’s like giving Mother Nature a standing ovation while we build our machines.
The Final Masterpiece
In the grand finale, after the panels are designed, fabricated, and tested, the machine is ready for action. It’s like watching a movie after understanding the script, the set, and the rehearsals. The panels are the unsung heroes, quietly orchestrating the entire performance.
Practical Application
Let’s imagine you’re running a factory, and you’ve just learned about Mastering Panel Design and Fabrication. Applying this knowledge, you decide to upgrade your machinery. By carefully designing and fabricating efficient control panels, you streamline production, reducing errors and increasing output. The practical result? A more productive and cost-effective manufacturing process.
Real-world Impact
Consider a car manufacturing plant that adopts the principles of Mastering Panel Design and Fabrication. The impact is real – machines operate with precision, reducing assembly time. This efficiency not only increases the number of cars produced but also improves overall product quality. In the real world, this means more affordable and reliable vehicles for consumers.
“Efficiency is not just a goal; it’s the heartbeat of successful manufacturing.”
Conclusion
Mastering Panel Design and Fabrication in Industrial Manufacturing is a symphony of creativity, precision, and innovation. It’s not just about making machines; it’s about crafting the future of industry. So, the next time you see a machine at work, remember the dance happening behind those panels – the dance that keeps our world moving forward.